HTML
CSS
Psychology
Mental Health
Styling
Self-Improvement
兒童積極自我對話:建立韌性與樂觀
識別和處理負面自我對話模式
了解負面自我對話的根源
負面自我對話,對許多兒童而言是一種常見的經驗,其根源往往來自多種因素的綜合。這些因素可能包括
提升正面自我對話的實用練習
識別負面自我對話模式
孩子,就像成人一樣,經常不自覺地進行負面自我對話。這種內心對話可以以各種形式出現,從唉
Read more about 兒童積極自我對話:建立韌性與樂觀
- 理解正念:學習正念的本質,作為一種工具,讓你活在當下,充分參與每一個瞬間。
- 正念冥想的好處:發現正念如何減輕壓力和焦慮、增強專注力以及促進更健康的人際關係。
- 開始行動:簡單的步驟,建立適合你生活的正念冥想日常。
- 每日融入正念:如正念行走和專注呼吸等技巧,以提升你的日常體驗。
- 克服挑戰:應對維持穩定正念練習中的常見障礙的小貼士。
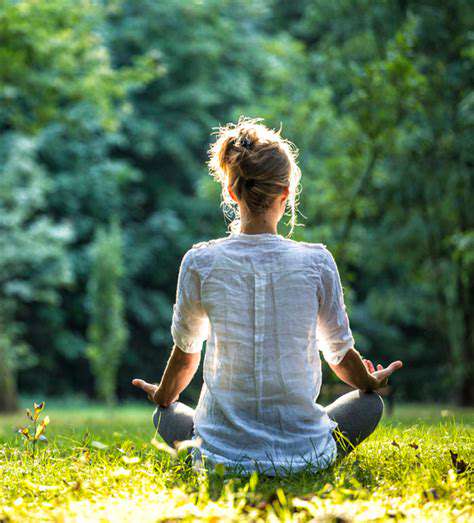
通過正念生活,提高你的心理健康、自我意識和情感韌性。加入越來越多的改變生活的社區,一步一腳印地改變自己。今天就擁抱正念,為更加充實的明天做好準備!
Nov 25, 2024
探索自然與心理健康在學前教育中的重要聯繫。發現接觸自然環境如何增強兒童的情感健康、創造力和認知發展。我們的文章深入探討了整合自然啟發學習環境的好處,鼓勵獨立探索,以及解決城市與自然之間的鴻溝。了解如何設計包容性的綠色空間以及城市綠化對兒童發展的積極影響。為教育工作者和家庭提供策略,以培養學前兒童的獨立性和對環境的欣賞。與我們一起促進心理健康,培養年輕學習者與自然的終身聯繫!
Jan 18, 2025