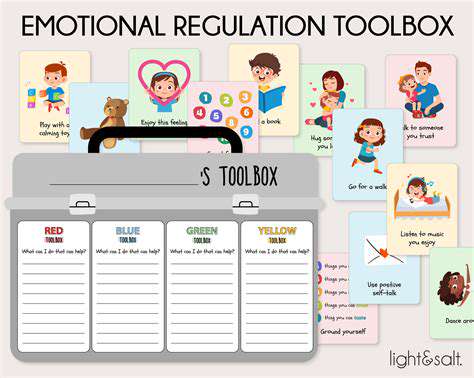
Child Development
Emotional Intelligence
Psychological Well-being
Problem Solving
Human Interaction
子供の情動知能:子供の感情を育む
最初のステップ

View Blog>>
感情語彙の理解
子供の感情的認識を育てる際、感情を特定し、名前を付けることは、不可欠な基礎となります。「イライラしている」のような一般的な言葉を使う代わりに、保育者は子供たちを正確な感情表現へと導くべきです:あなたは
感情調整戦略の開発
感情調整の重要性理解
感情調整スキルは、精神的な健康と社会的な成功の基盤を形成します。これらの能力により、子供たちは様々な状況を乗りこなし、
共感:他者の立場に立つ

感情体験の多様性を理解する
真の共感とは、共通の感情を持つこと以上のことを意味します。それは、他者の感情を理解することを必要とします。
レジリエンスの構築:挫折からの反発

Read more about 子供の情動知能:子供の感情を育む
持続可能な生活の社会的および経済的利益 持続可能な生活の深い社会的および経済的利点を発見してください。この包括的なガイドでは、ロールプレイが子供の社会的スキルと情緒的成長をどのように促進し、それを持続可能な実践のより広い文脈と関連付けるかを探ります。 社会的スキルの向上 ロールプレイが子供たちのコミュニケーション、協力、共感をどのように発展させ、強い人間関係と感情的知能の基礎を築くのかを学びます。 認知的成長 ロールプレイの認知的利点を探求し、想像力、問題解決能力、生涯にわたる学習のための好奇心を促す方法を理解します。 感情的レジリエンス 様々なシナリオを演じることで、子供たちが感情を表現し、課題に対処し、感情的な健康を高める手助けをする方法を理解します。 持続可能性の経済的影響 持続可能な実践がもたらす経済的利益、企業のコスト削減やグリーン経済での雇用成長を詳しく見ていきます。 社会的責任 持続可能な実践が地域社会をどのように高め、社会的平等を促進し、共同の責任感を通じて所属感を育むのかを学びます。 課題の克服 持続可能な実践を実施する際の障害を克服するための戦略を発見し、政府、企業、地域社会の協力の重要性を強調します。 今日は持続可能な生活への旅を始め、より健康的な地球に貢献しながら、社会的および経済的福祉を向上させましょう。
Jan 01, 2025
より健康的な地球のために持続可能な生活を取り入れましょう。メタ説明:持続可能な生活の重要性と影響を発見します。カーボンフットプリントを減らし、健康な地球に貢献するための実用的なステップ、エコフレンドリーな実践、革新的なソリューションを学びましょう。意識的な選択があなたのライフスタイルとコミュニティにどのように利益をもたらすかを探り、環境保護と社会的公正を促進します。今日、持続可能性の運動に参加しましょう!キーワード:持続可能な生活、エコフレンドリーな実践、気候変動、再生可能エネルギー、意識的な消費、コミュニティ参加、環境影響。コンテンツ概要:このページは、持続可能な生活とそれが今日の世界で重要である理由についての深い理解を提供します。資源消費を減少させ、気候変動に立ち向かう必要性を強調し、持続可能なライフスタイルを採用するために個人が取るべき実用的なステップを概説します。グリーンライフスタイルの利点は環境保護を超えて、コスト削減、健康改善、コミュニティ参加を含みます。さらに、エコフレンドリーな実践を強化する革新的な解決策を探求し、読者に知識を共有し、持続可能な文化を育むよう促します。これらの実践を取り入れることで、私たちは次世代のために繁栄する地球を確保する共同の影響を生み出すことができます。
Jan 10, 2025
幼児教育における聴く力の重要性を探求します。アクティブリスニングがコミュニケーション、共感、批判的思考をどのように育むのかを理解します。言語発達や情緒的知識をサポートする魅力的なリスニング環境を作るための戦略を発見します。マインドフルネス、運動、感覚体験が幼児教育環境での集中力と参加をどのように向上させるかを学びます。教育者に対し、アクティブリスニングを促進し、支援的なコミュニケーション環境を作り、構造的なルーチンを実施するための効果的な技術を提供します。若い学習者の聴く能力を育むための教育者と親の重要な役割について深く掘り下げ、彼らの生涯の成功を支えます。
Feb 07, 2025
つながりを築く上での共感と忍耐の重要性個人および職業環境において深く意味のあるつながりを育むための共感と忍耐の重要性を探ります。他者の感情を共有し、理解する能力である共感が、いかにして関係の堅固な基盤を築き、感情知能を高め、真の対話を促進するのかを理解します。アクティブリスニング、マインドフルネス、反省的実践を通じて共感を育む実践的な戦略を学びます。忍耐力が効果的なコミュニケーション、紛争解決、強力なチームダイナミクスにどのように寄与するのかを発見し、職場でのコラボレーションやイノベーションを高めます。これらの重要なスキルを身につけ、対話を豊かにし、持続的な充実感と成功をもたらす深い関係を築きましょう。
Feb 23, 2025
幼児期におけるルーチンの重要性メタ説明:幼児の発達におけるルーチンの重要な役割を発見してください。一貫した日常スケジュールを確立することで、安心感を促進し、学習を向上させ、子供の健康な習慣を育成する方法を学びましょう。感情的および身体的な健康を育む成功し柔軟なルーチンを実装するためのヒントを探求してください。---一貫したルーチンの確立は、子供にとって非常に重要であり、彼らに安心感と予測可能性を提供します。このアーティクルでは、ルーチンの多くのメリット、改善された行動、健康的な睡眠パターン、強化された学習体験に深く切り込みます。また、これらの構造内に柔軟性を組み込むことの重要性についても議論し、子供が生活の変化に優雅に対処できるよう支援します。一貫した睡眠スケジュールの確立からバランスの取れた食事と定期的な身体活動を奨励することなど、成功した日常ルーチンを作成するための実用的なヒントを探ります。マインドフルネスの実践が子供の感情的な認識をサポートする方法を学びましょう。子供が成長するにつれて、必要な生活スキルを備え、健康な習慣と回復力に向けた基盤を築きましょう。しっかりとしたルーチンがあなたの子供の発達と幸福にどのように大きく寄与できるかを理解するために、読み進めてください!
Mar 07, 2025
幼児期に共感力と慈悲心の土台を築くことは、バランスのとれた人間育成にとって非常に重要です。研究によると、共感力と慈悲心を学ぶ子供は、より愛情深く責任感を持つ人へと成長する可能性が高いことが示されています。
Apr 09, 2025
1. 感情の承認:子供の感情を認め、支えとなる環境を作ります。
2. ルールの確立:一貫したルールは変化の時期に安定感と安全感をもたらします。
3. コミュニケーションの促進:オープンなコミュニケーション
Apr 19, 2025