Child Development
Well-being
Empty
Unanalyzable
EmotionalIntelligence
RelationshipManagement
Early Childhood Education
Soziale Fähigkeiten für kleine Kinder: Ihrem Kind helfen, in Gruppen zu gedeihen
Die Bedeutung der sozial-emotionalen Entwicklung im frühen Kindesalter
Das Verständnis der Grundlagen
Sozial-emotionale Entwicklung im frühen Kindesalter legt den Grundstein für zukünftigen Erfolg und beeinflusst alles, von der akademischen Leistung bis zu...
Erkennung und Bewältigung frühzeitiger sozialer Herausforderungen

Das Verständnis der Bedeutung früher Anzeichen
Die frühzeitige Erkennung signifikanter Probleme ist entscheidend für eine effektive Intervention
Förderung von emotionaler Intelligenz und Empathie

Emotionale Intelligenz verstehen
Emotionale Intelligenz (EQ) ist ein entscheidendes Kompetenzset, um die Komplexitäten des Alltags zu meistern
Förderung positiver sozialer Interaktionen in verschiedenen Kontexten
Förderung der Zusammenarbeit in Spielgruppen
Spielgruppen sind entscheidend für die Förderung sozialer Fähigkeiten bei jungen Kindern. Die Förderung der Zusammenarbeit in diesen Kontexten
Read more about Soziale Fähigkeiten für kleine Kinder: Ihrem Kind helfen, in Gruppen zu gedeihen
Soziale und wirtschaftliche Vorteile nachhaltigen Lebens Entdecken Sie die tiefgreifenden sozialen und wirtschaftlichen Vorteile eines nachhaltigen Lebensstils. Dieser umfassende Leitfaden untersucht, wie Rollenspiele die sozialen Fähigkeiten und das emotionale Wachstum von Kindern fördern und dies mit dem breiteren Kontext nachhaltiger Praktiken verbindet. Verbesserung sozialer Kompetenzen Erfahren Sie, wie Rollenspiele die Kommunikation, Kooperation und Empathie unter Kindern entwickeln und so die Grundlage für starke Beziehungen und emotionale Intelligenz schaffen. Kognitive Entwicklung Erkunden Sie die kognitiven Vorteile des Rollenspiels, das kreatives Denken, Problemlösungsfähigkeiten und eine neugierige Haltung für lebenslanges Lernen anregt. Emotionale Resilienz Verstehen Sie, wie das Durchspielen verschiedener Szenarien den Kindern hilft, ihre Emotionen auszudrücken, Herausforderungen zu bewältigen und ihr emotionales Wohlergehen zu verbessern. Ökonomische Auswirkungen der Nachhaltigkeit Vertiefen Sie sich in die wirtschaftlichen Vorteile nachhaltiger Praktiken, einschließlich der Kostensenkung für Unternehmen und des Jobwachstums in der grünen Wirtschaft. Soziale Verantwortung Lernen Sie, wie nachhaltige Praktiken Gemeinschaften stärken, soziale Gerechtigkeit fördern und ein Zugehörigkeitsgefühl durch kollektive Verantwortung schaffen. Herausforderungen überwinden Entdecken Sie Strategien zur Überwindung von Hindernissen bei der Umsetzung nachhaltiger Praktiken und betonen Sie die Zusammenarbeit zwischen Regierungen, Unternehmen und Gemeinschaften. Beginnen Sie noch heute Ihre Reise zu einem nachhaltigen Lebensstil und tragen Sie zu einem gesünderen Planeten bei, während Sie Ihr soziales und wirtschaftliches Wohlbefinden verbessern.
Jan 01, 2025
Die Bedeutung der Förderung der Unabhängigkeit bei Kindern Metabeschreibung: Entdecken Sie die wesentlichen Vorteile der Förderung der Unabhängigkeit bei Kindern. Lernen Sie praktische Strategien zur Förderung von Selbstständigkeit, Selbstbewusstsein und Problemlösungsfähigkeiten. Schaffen Sie eine unterstützende Umgebung, die Resilienz und kritisches Denken fördert.--- Die Förderung der Unabhängigkeit bei Kindern ist ein wesentlicher Aspekt ihrer Entwicklung. Dieser umfassende Leitfaden untersucht die zahlreichen Vorteile, die Selbstständigkeit zu fördern, einschließlich der Stärkung des Selbstwertgefühls und der Kritischen Denkfähigkeiten. Erfahren Sie, wie Sie altersgerechte Verantwortlichkeiten umsetzen, klare Erwartungen setzen und konstruktives Feedback geben, um ein Gefühl von Autonomie bei Ihren Kindern zu entwickeln. Entdecken Sie praktische Ansätze, um Kinder bei der Bewältigung von Herausforderungen zu unterstützen und ihre Entscheidungsfähigkeit zu verbessern. Durch ansprechende Aktivitäten im Freien und das Ermutigen kleiner Aufgaben können Sie das Selbstbewusstsein und die Problemlösungsfähigkeiten Ihres Kindes stärken. Finden Sie heraus, wie Sie eine strukturierte, aber flexible häusliche Umgebung schaffen können, die Unabhängigkeit fördert und gleichzeitig die notwendige Unterstützung bietet. Wichtige Themen: - Die Bedeutung der Unabhängigkeitsförderung - Praktische Strategien zur Förderung der Selbstständigkeit - Selbstbewusstsein durch unabhängige Aufgaben stärken - Die Auswirkungen eines unterstützenden familiären Umfelds Erkunden Sie unseren Artikel, um Ihre Kinder zu ermächtigen und ihnen die Fähigkeiten zu vermitteln, die sie für eine erfolgreiche und resiliente Zukunft benötigen.
Jan 18, 2025
Erforschen Sie die wesentliche Verbindung zwischen Natur und psychischem Wohlbefinden in der Vorschulerziehung. Entdecken Sie, wie die Exposition gegenüber natürlichen Umgebungen die emotionale Gesundheit, Kreativität und kognitive Entwicklung von Kindern verbessert. Unser Artikel beleuchtet die Vorteile der Integration von naturinspiriertem Lernen, fördert unabhängige Erkundungen und geht der Kluft zwischen Stadt und Natur nach. Erfahren Sie, wie man inklusive grüne Räume gestaltet und die positiven Auswirkungen von urbaner Begrünung auf die kindliche Entwicklung nutzt. Ausstatten Sie Pädagogen und Familien mit Strategien zur Förderung von Unabhängigkeit und Umweltbewusstsein bei Vorschulkindern. Schließen Sie sich uns an, um das psychische Wohlbefinden zu fördern und eine lebenslange Verbindung zur Natur bei jungen Lernenden zu entwickeln!
Jan 18, 2025
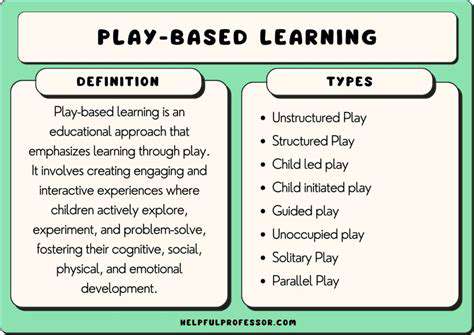
Entdecken Sie die transformative Kraft des spielbasierten Lernens für kleine Kinder! Unser ausführlicher Artikel untersucht, wie das Engagement im Spiel die kognitive Entwicklung fördert, emotionale und soziale Fähigkeiten verbessert und eine Liebe zum Lernen weckt. Erfahren Sie mehr über die Vorteile von Spielen im Klassenzimmer, einschließlich verbesserter Problemlösungsfähigkeiten, Kreativität und Resilienz. Wir geben Einblicke in die Gestaltung effektiver spielbasierter Lernumgebungen und praktische Implementierungsstrategien für Pädagogen. Dieser Leitfaden, der Zusammenarbeit und Anpassungsfähigkeit betont, ist unerlässlich für Lehrer, die eine interaktive und bereichernde Lernerfahrung fördern möchten. Entfalten Sie noch heute das Potenzial des Spiels im Lernen!
Jan 19, 2025
Einen sicheren und anregenden Lernraum für Vorschulkinder schaffen. Stellen Sie sicher, dass Ihre Vorschulkinder gedeihen, indem Sie einen sicheren und ermutigenden Lernraum gestalten. Entdecken Sie die Bedeutung von physischer und emotionaler Sicherheit und wie diese Elemente die kognitive Entwicklung und die Unabhängigkeit junger Lernender fördern. Setzen Sie effektive Strategien um, um eine sichere Umgebung und strukturierte Routinen zu schaffen, die Selbstdisziplin fördern, die Entwicklung sozialer Fähigkeiten unterstützen und die Liebe zum Lernen anregen. Erkunden Sie, wie Sie mit ansprechenden Ressourcen und spielbasierten Lernaktivitäten die Neugier anregen können, die die Bildungserfahrungen der Kinder bereichert. Lernen Sie, wie man Resilienz durch eine Wachstumsmentalität fördert, die die Kinder dazu befähigt, Herausforderungen als Wachstumschancen zu betrachten. Besuchen Sie unsere Website, um Techniken zu entdecken, die ein Umfeld schaffen, in dem Vorschulkinder sich sicher, inspiriert und begeistert von ihrer Bildungspfad fühlen.
Mar 09, 2025
Wie man mit häufigen Kindheitsängsten und Phobien umgeht
Apr 29, 2025
Frühzeitige Erkennung von ADHS-Merkmalen bei Vorschulkindern
May 01, 2025
Verantwortung durch altersgerechte Hausarbeiten lehren
May 05, 2025
Die kulturellen Einflüsse auf Erziehungsstile erforschen
May 09, 2025
Schaffung einer familiären Umgebung, die offene Teilung fördert
May 09, 2025
Humor und Positivität in die täglichen Herausforderungen der Elternschaft integrieren
May 09, 2025
Effektive Erziehungstechniken: Aufbau einer liebevollen Familienatmosphäre
Jun 24, 2025