إدارة المشاجرات بين الأشقاء: تعزيز الحلول السلمية
Implementing Fair and Consistent Rules

Implementing Robust and Ethical AI Models
Developing AI models that are fair and consistent requires a multi-faceted approach that goes beyond simply achieving high accuracy. A crucial element is careful consideration of the data used to train the model, ensuring that it doesn't perpetuate existing biases or reflect historical injustices. This necessitates identifying and addressing potential sources of bias in the training dataset and actively working to collect and incorporate diverse data points.
Furthermore, the model's architecture and algorithms should be designed with fairness and consistency in mind. Techniques like adversarial debiasing and fairness-aware learning can be employed to mitigate biases that might emerge during the model's operation. This proactive approach is essential to ensure that the model's predictions and outputs are not skewed towards particular groups or individuals.
Ensuring Data Quality and Transparency
The quality of the data used to train AI models is paramount to their fairness and consistency. Data that is incomplete, inaccurate, or biased will inevitably lead to models that reflect and amplify those flaws. Thorough data cleaning, validation, and augmentation processes are essential to ensure data accuracy and reliability. This meticulous attention to data quality is fundamental to building trustworthy and ethical AI systems.
Moreover, transparency in the model's decision-making process is crucial. Users and stakeholders need to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions. Clear documentation and explainable AI (XAI) techniques can provide insights into the model's reasoning, thereby fostering trust and accountability.
Establishing Clear Evaluation Metrics and Monitoring Procedures
Defining and implementing appropriate evaluation metrics is critical to assess the fairness and consistency of AI models. These metrics should not only focus on accuracy but also consider fairness across different demographic groups, ensuring that the model performs equitably for all. For example, metrics like equal opportunity and disparate impact should be incorporated into the evaluation process. This approach allows for continuous monitoring and evaluation.
Furthermore, implementing robust monitoring procedures to track the model's performance over time is essential. This allows for identification of potential drift or bias over time and provides opportunities for remedial action.
Addressing Potential Bias and Discrimination
A critical component of implementing fair and consistent AI models is recognizing and addressing potential bias. Identifying potential bias and discrimination in the data, algorithms, or deployment environment is essential. Regular audits, testing, and evaluation should be conducted to detect and mitigate bias. This proactive approach to bias detection is key to ensuring that AI systems are fair and just.
Mediation and Conflict Resolution Techniques
Understanding Sibling Conflict
Sibling rivalry is a common and often inevitable part of growing up. Understanding the underlying causes of sibling conflict is crucial for effective mediation. Sometimes, disagreements stem from competition for parental attention, differing personalities, or differing needs. Recognizing these underlying dynamics can help parents approach conflict resolution with more empathy and understanding, leading to more constructive outcomes.
Recognizing the specific triggers and patterns of conflict between siblings can be incredibly helpful. Are there certain toys or activities that consistently spark disputes? Do specific personalities clash more frequently? Identifying these patterns allows for proactive strategies to prevent future conflicts. For instance, establishing clear rules around shared resources can help avoid disputes over toys or space.
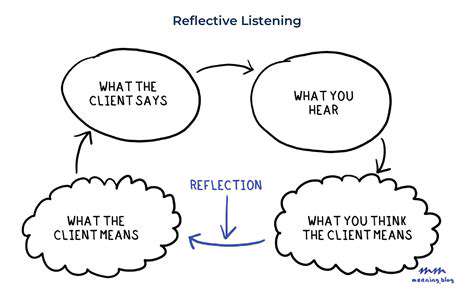
Active Listening and Empathy
Mediation relies heavily on active listening. Parents need to listen attentively to each sibling's perspective without interrupting or judgment. Creating a safe space where siblings feel heard and understood is key. Empathy plays a crucial role in this process. Encouraging siblings to see things from each other's point of view fosters understanding and encourages a sense of shared responsibility.
Role-playing can be a valuable tool in developing empathy. Ask siblings to imagine how their actions might affect the other person. This can help them understand the emotional impact of their behavior, promoting a more compassionate approach to conflict resolution. Encourage siblings to express their feelings and validate those feelings, even if they disagree on the underlying issue.
Establishing Ground Rules and Expectations
Clear and consistent rules are essential for managing sibling conflict. These rules should be age-appropriate and clearly communicated, covering issues like sharing, taking turns, and respecting each other's belongings. Consistency in enforcing these rules is critical for establishing a predictable and respectful environment.
Establishing expectations for behavior during disagreements can also help. For example, encourage siblings to use I feel statements to express their emotions and avoid personal attacks. These ground rules create a framework for respectful communication and conflict resolution, setting the stage for productive discussions.
Conflict Resolution Strategies
Various conflict resolution strategies can be employed, depending on the nature and severity of the conflict. Simple techniques, such as taking a break or using a designated calming space, can be effective for de-escalating tense situations. Encouraging compromise and finding solutions that satisfy both parties is another important step towards resolving conflicts peacefully.
Emphasize problem-solving skills. Help siblings brainstorm solutions to their disagreements. Encourage them to consider options that benefit everyone involved, fostering cooperation and a sense of shared responsibility for finding solutions.
Promoting Positive Interactions
Creating opportunities for positive interactions between siblings can help strengthen relationships and reduce conflict. Engaging in activities together, like playing games, watching movies, or engaging in shared hobbies, can foster a sense of camaraderie and shared experiences.
Focus on rewarding positive behaviors. When siblings demonstrate cooperation, empathy, or respect, acknowledge and praise these positive interactions. Reinforcing positive behaviors creates a more supportive and encouraging environment for future interactions. This helps build healthy sibling relationships.
Mediation Techniques for Parents
Parents play a crucial role in mediating sibling disputes. Active listening, empathy, and clear communication are essential skills for parents to employ when mediating. Creating a safe space where siblings feel comfortable expressing their feelings is key to effective mediation.
Remain neutral and avoid taking sides. Focus on helping siblings understand each other's perspectives and work towards solutions that satisfy everyone. Using specific language to help siblings understand each other's feelings, and the impact of their actions, can lead to more productive conflict resolution.
Long-Term Strategies for Preventing Conflict
Preventing future conflicts requires a proactive approach that builds healthy sibling relationships. Establishing routines and clear expectations for sharing and responsibilities can help avoid misunderstandings. Building a strong sense of family unity and shared values can also reduce conflict.
Regular family meetings can be a powerful tool for open communication and addressing concerns. These meetings provide a platform for siblings to voice their needs and concerns in a structured and respectful manner. This can be highly effective in preventing future conflicts.
Encouraging Empathy and Perspective-Taking
Understanding Different Perspectives
Sibling rivalry is a common experience, often fueled by differing perspectives on shared resources, attention, and even perceived injustices. Recognizing that each sibling views situations through their own lens, shaped by their unique experiences and developmental stages, is crucial for effective intervention. Empathy, the ability to understand and share the feelings of another, is a cornerstone of conflict resolution. Helping siblings articulate their feelings and consider the other's viewpoint, even if they don't agree, can significantly reduce tension and promote understanding.
For instance, one sibling might feel resentful if another consistently gets more attention. Understanding this feeling, without necessarily agreeing with it, allows parents to address the underlying need for connection and fairness. A parent can then facilitate a conversation where each sibling can express their feelings without interruption, fostering a sense of validation and encouraging empathy for the other's perspective.
Promoting Active Listening and Communication
Active listening is a vital skill for navigating sibling conflicts. It involves more than just hearing the words; it includes paying close attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues, reflecting back what is heard, and asking clarifying questions to ensure a complete understanding. This process fosters a sense of being heard and understood, which is essential for de-escalating tension and promoting cooperation. By practicing active listening, parents can help their children develop crucial communication skills that extend far beyond the sibling dynamic.
Encouraging open and honest communication between siblings is equally important. Creating a safe space where siblings feel comfortable expressing their needs and concerns without fear of judgment or retaliation is paramount. This might involve establishing clear communication guidelines, such as taking turns speaking, using I feel statements, and avoiding name-calling or personal attacks. These skills will serve them well in future relationships and interactions.
Encouraging Collaborative Problem-Solving
Instead of immediately stepping in to resolve conflicts, parents can encourage siblings to find solutions together. This approach empowers them to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, while also fostering a sense of shared responsibility for finding solutions that work for everyone. Presenting scenarios and prompting questions that require them to think creatively about solutions can be powerful tools for encouraging this type of collaborative approach. For example, if siblings are arguing over who gets to use a certain toy, parents can guide them to brainstorm alternative solutions, such as taking turns, playing with different toys, or finding a way to share the toy simultaneously.
This approach not only helps resolve the immediate conflict but also builds valuable skills for navigating disagreements in the future. By fostering a sense of shared responsibility and mutual respect, parents can equip their children with the tools they need to effectively manage conflicts and build stronger, more harmonious relationships.