Supporting Every Developmental Milestone: A Parent's Handbook
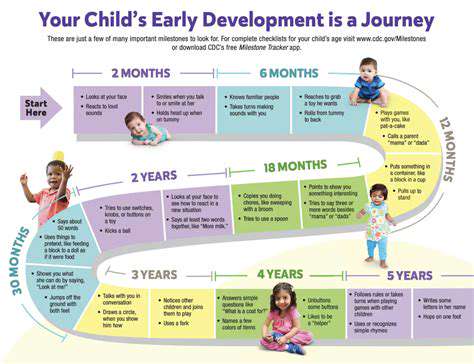
Understanding Developmental Milestones
Developmental milestones are significant physical, cognitive, social, and emotional skills that children typically acquire at certain ages. These milestones provide a general guideline for how children develop, helping parents and professionals identify potential delays or areas that might require further attention. Understanding these milestones is crucial for ensuring a child's healthy development and identifying any potential concerns early on. It's important to remember that every child develops at their own pace, and some variations are perfectly normal.
There are many different milestones, and they vary depending on the age range. While a one-year-old might be expected to walk independently, a six-month-old is expected to be able to hold their head up. These milestones are a way to measure the child's progression and ensure that they are on track. Knowing what to expect at different stages of development can help parents and caregivers feel more confident and support their children's growth.
Identifying Potential Delays
While some variations in development are normal, consistent delays in reaching certain milestones may warrant further evaluation. These delays could indicate an underlying condition, and early intervention is critical for maximizing a child's potential. Parents or caregivers should pay attention to any noticeable differences in a child's development compared to peers, and consult with a pediatrician or other healthcare professional if they have concerns.
It's important to remember that identifying potential delays is not about labeling a child. It's about proactively seeking support and ensuring the child receives the necessary resources to thrive. Regular checkups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential to monitor development and address any concerns promptly.
Monitoring Physical Development
Physical development encompasses various skills, from gross motor skills like walking and running to fine motor skills like grasping and manipulating objects. Monitoring these skills is important to ensure that a child is developing appropriately and meeting their physical potential. Parents should observe their child's ability to perform different activities and compare them to typical milestones for their age group.
Regular checkups with a pediatrician are crucial to assess a child's physical development. During these visits, pediatricians will evaluate a child's growth, strength, and reflexes to identify any potential issues. Early intervention for physical developmental delays can significantly improve a child's overall well-being and future prospects.
Recognizing Cognitive and Social-Emotional Development
Cognitive development involves acquiring knowledge, problem-solving skills, and language abilities. Social-emotional development focuses on building relationships, expressing emotions, and understanding social cues. These areas are equally important to physical development and require consistent monitoring. As children grow, observe their interactions with others, their communication skills, and their ability to engage in imaginative play.
Parents and caregivers can actively engage in activities that foster cognitive and social-emotional development, such as reading stories, playing games, and engaging in conversations. These interactions not only support development but also strengthen the parent-child bond. By creating a nurturing environment, parents can help children thrive in both their cognitive and social-emotional growth.
Supporting Cognitive Development: Nurturing Curiosity and Learning
Fostering a Growth Mindset
Cultivating a growth mindset is crucial for cognitive development. Encouraging children to view challenges as opportunities for learning, rather than setbacks, empowers them to embrace new experiences and persevere through difficulties. This approach fosters resilience and a deep understanding that intelligence and abilities can be developed through dedication and effort. A supportive environment where mistakes are seen as learning opportunities fosters a love of learning and a willingness to take risks, essential building blocks for cognitive growth.
Encouraging Exploration and Discovery
Providing ample opportunities for exploration and discovery is paramount to nurturing curiosity. This can involve hands-on activities, engaging in nature, visiting museums, or simply allowing children to explore their surroundings. These experiences stimulate curiosity and allow children to develop their own understanding of the world around them. By encouraging independent exploration and questioning, we ignite a lifelong passion for learning and discovery, a fundamental aspect of cognitive development.
The Power of Questioning
Encouraging children to ask questions is vital for cognitive development. Questioning is a natural part of learning and understanding. By actively listening to and responding to their inquiries, we demonstrate that their questions matter and that exploration of ideas is valued. This fosters a sense of intellectual curiosity and encourages critical thinking skills, essential elements in navigating the complexities of the world.
The Role of Play in Cognitive Development
Play is a powerful tool for cognitive development. Through play, children engage in problem-solving, creativity, and imagination. This process allows children to experiment with different ideas, develop social skills, and refine their understanding of the world. Structured and unstructured play activities, from building blocks to imaginary scenarios, provide rich learning experiences that stimulate cognitive growth.
Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
A supportive learning environment is essential for nurturing curiosity and promoting cognitive development. This means creating a safe and encouraging space where children feel comfortable taking risks, asking questions, and exploring their ideas without fear of judgment. Open communication, active listening, and positive reinforcement all contribute to a supportive environment where children thrive cognitively and emotionally.
The Importance of Social Interaction
Social interaction plays a significant role in cognitive development. Interacting with peers and adults exposes children to diverse perspectives, different ways of thinking, and new ideas. Social interactions allow children to learn from others, negotiate, and develop crucial communication and collaboration skills. These skills are essential for navigating the social world and are deeply intertwined with cognitive growth, fostering a holistic development.