Maximizing Learning Through Play Based Approaches in Early Childhood Education
The Benefits of Play-Based Learning
Enhancing Cognitive Development Through Play
Play-based learning is instrumental in bolstering cognitive development in young children. Engaging in play not only captures their interest but also stimulates critical thinking and problem-solving skills. When children are given the freedom to explore, they learn to associate cause and effect, which is fundamental to scientific reasoning. Simple actions like stacking blocks and figuring out how to balance them require children to strategize and make quick decisions, greatly enhancing their analytical skills.
Moreover, during play, children naturally encounter challenges that encourage them to think creatively and adaptively. For instance, while building a fort with cushions, they must consider stability and structure, applying their understanding of physics without even realizing it. This environment nurtures an intrinsic motivation to learn as the benefits of mastering a new concept become apparent through experiential learning. Thus, play provides a robust platform for early cognitive skills to flourish in a relaxed and enjoyable setting.
Furthermore, the social dimension of play-based learning cannot be overlooked. Interacting with peers during play introduces children to various perspectives and collaborative problem-solving. They learn to articulate their ideas, listen to others, and develop negotiation skills. Such collaborative play experiences are vital in fostering not only cognitive prowess but also essential social-emotional skills that contribute to a well-rounded education. As such, the interplay of cognitive challenges and social interactions during play serves to maximally enhance learning outcomes for young children.
Fostering Emotional and Social Skills
Play-based learning offers a unique avenue for children to develop emotional intelligence. Through role-playing and imaginative games, children explore different scenarios that allow them to express a wide range of emotions. This safe outlet helps them identify their feelings and recognize the emotions of their peers, fostering empathy and understanding. For instance, by taking on various characters during pretend play, children can navigate complex social situations and learn appropriate emotional responses.
Additionally, these play scenarios often require cooperation and teamwork, further enhancing children's social skills. Whether it’s building a group project in arts and crafts or organizing a game with friends, kids must communicate, cooperate, and sometimes negotiate. These experiences build a foundation for strong interpersonal skills, important for their interactions throughout life. Children learn to value teamwork, work through differences, and celebrate collective successes, all of which are vital attributes in both academic and personal realms.
Moreover, play-based learning helps in cultivating resilience as children face challenges during their playtime activities. They may experience setbacks, such as a toy breaking or losing a game, and through these challenges, they learn to cope with disappointment and find alternative solutions. By navigating these emotions and experiences, children build significant emotional resilience. This process equips them with the skills needed to handle real-life obstacles, making play not just enjoyable but a critical component in developing strong, adaptable individuals.
Implementing Play-Based Learning in the Classroom
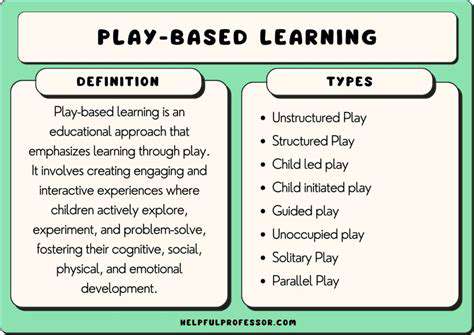
Understanding the Benefits of Play-Based Learning
Research has consistently shown that play-based learning is an effective method for early childhood education, enabling students to develop essential skills and knowledge while fostering a love for learning. By incorporating play into the classroom, educators can create an engaging and interactive environment that promotes active participation and hands-on exploration. This, in turn, can help improve academic performance, social skills, and cognitive abilities in children.
Moreover, play-based learning can have numerous long-term benefits for students, such as enhanced creativity, problem-solving skills, and emotional intelligence. Furthermore, this approach to education can also help reduce stress and anxiety in children, promoting a positive attitude towards learning and academic achievement.
Designing Play-Based Learning Environments
A well-crafted play-based learning environment requires careful planning and execution to ensure that students can engage in meaningful and interactive experiences.
Key considerations in designing such environments include providing a range of hands-on materials and resources, setting up play-based zones and areas, and incorporating technology and digital tools to support learning. Educators should strive to create spaces that are adaptable, flexible, and tailored to the diverse needs and interests of their students.
Implementing Play-Based Learning in Practice
Implementing play-based learning in practice can be a challenging yet rewarding experience for educators. A crucial aspect is to strike a balance between structure and flexibility, allowing students to explore and learn while also providing clear guidance and support.
Teachers should aim to use open-ended and inquiry-based approaches to encourage students to take an active role in their learning, exploring questions and problems, and developing solutions through play-based activities. By doing so, educators can foster a sense of autonomy, curiosity, and engagement in learning, leading to improved academic outcomes and a lifelong love of learning.
Overcoming Challenges and Building Collaborative Relationships
While play-based learning offers numerous benefits, it can also present challenges for educators, particularly in terms of assessing student progress and managing the classroom environment.
One effective strategy for overcoming these challenges is to establish collaborative relationships with colleagues, sharing best practices and expertise to support the development of play-based learning environments. By working together, educators can develop a shared understanding of the benefits and challenges of play-based learning and create a supportive community of practice that promotes teacher growth and student success.