HTML
Styling
CSS
child development
fine motor skills
Early Childhood Development
Multisensory Learning
Compreendendo o Brinquedo Sensorial: Benefícios para o Desenvolvimento
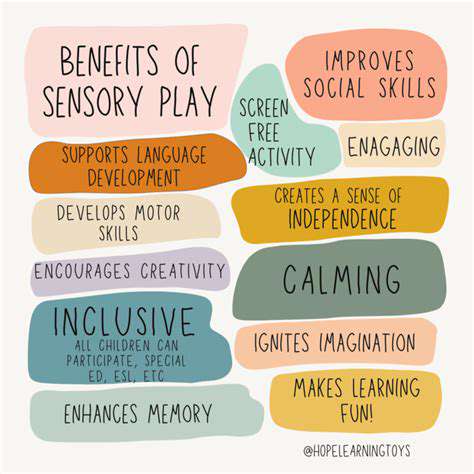
Cultivando Habilidades Motoras Finais Através da Exploração Tátil

Desenvolvendo Destreza Através do Brincar
Aprimorando as Habilidades de Linguagem e Comunicação por Meio de Experiências Sensoriais Experiências sensoriais desempenham um papel crucial no desenvolvimento de habilidades de linguagem e comunicação, particularmente na primeira infância
Explorando a Abordagem Multissensorial
Read more about Compreendendo o Brinquedo Sensorial: Benefícios para o Desenvolvimento
O Papel Crítico da Socialização Precoce Explore o papel essencial da socialização precoce no desenvolvimento das crianças, destacando como as interações iniciais moldam suas habilidades sociais, inteligência emocional e adaptabilidade. Este artigo examina o impacto dos estilos de parentalidade, das relações entre pares e dos ambientes educacionais no desenvolvimento da personalidade. Aprenda como experiências sociais positivas melhoram a empatia, a cooperação e a comunicação, estabelecendo a base para relacionamentos adultos saudáveis. Compreenda os efeitos de longo prazo das amizades infantis e da dinâmica familiar na competência social e no crescimento pessoal. Descubra estratégias práticas para cuidadores estimularem interações sociais saudáveis durante esses anos formativos. Palavras-chave: socialização precoce, desenvolvimento infantil, habilidades sociais, inteligência emocional, estilos de parentalidade, relações interpessoais, desenvolvimento da personalidade, ambientes educacionais.
Jan 13, 2025
Descubra o poder transformador da aprendizagem baseada em jogos na educação infantil. Este guia abrangente explora como o jogo serve como uma ferramenta crítica para o desenvolvimento cognitivo, crescimento social e emocional e aquisição de habilidades ao longo da vida. Aprenda sobre o papel vital que os educadores desempenham em promover experiências de aprendizagem envolventes e os benefícios de longo prazo de fomentar a curiosidade, criatividade e habilidades de resolução de problemas nas crianças. Descubra estratégias eficazes para implementar a aprendizagem baseada em jogos em ambientes educacionais e entenda como essa abordagem nutre alunos resilientes e motivados que prosperam academicamente e socialmente. Junte-se a nós para defender um ambiente educacional divertido e enriquecedor que prioriza a alegria do aprendizado!
Jan 19, 2025
A influência das interacções entre pares nas primeiras competências sociais
May 02, 2025
Por que a Consistência na Parentalidade Leva a Melhores Resultados
May 04, 2025
Gerenciando o estresse parental enquanto permanece presente para as crianças
May 06, 2025
Definir expectativas realistas para promover um crescimento equilibrado
May 06, 2025
Apresentando novas experiências para construir a confiança em crianças
May 07, 2025
Estratégias de Escuta Ativa que Fortalecem os Laços Parentais
May 09, 2025
Ensinar Gratidão: Criando Crianças Gratificadas e Compaixão
Jun 08, 2025
Conceitos Matemáticos para Pré-escolares: Tornando a Aprendizagem de Números Divertida
Jun 10, 2025
Gerenciamento Positivo de Comportamento: Disciplina Suave e Eficaz
Jun 24, 2025
Ensinar Resiliência Através de Histórias: Inspirando Coragem
Jul 03, 2025