Nurturing Natural Curiosity: The Key to Inspiring Lifelong Learning
The Inherent Drive for Learning
Understanding the Natural Instinct for Knowledge
The innate drive for learning is often likened to a primal instinct that every human being possesses. This natural curiosity is not merely a byproduct of social interaction but a fundamental aspect of our psyche. From the moment we are born, our senses are relentlessly receptive, absorbing information from the world around us. This impulse to seek out information and experiences informs our understanding of the environment and ultimately influences our growth and development.
As children, this unquenchable thirst for knowledge presents itself in myriad forms—through exploration, observation, and questioning. A toddler’s incessant queries about the world exemplify an instinctual response that plays a critical role in language acquisition, social skills, and cultural understanding. Thus, while learning is structured in formal educational settings, it primarily thrives in less formal, natural circumstances fueled by a child's curiosity.
Curiosity is closely linked to a broader spectrum of cognitive processes including critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving. Children who are encouraged to ask questions and explore freely can develop a more profound understanding of concepts, allowing them to employ knowledge in various contexts. The stimulation of this inherent drive can lead to a lifelong passion for learning, underlining the importance of nurturing curiosity in early stages of development.
With advancements in neuroscience, researchers have discovered that curiosity is not simply an emotional response; it's also a cognitive one that engages various brain regions associated with reward and information processing. Therefore, when curiosity is piqued, a series of neural pathways are activated that create positive reinforcement, making learning a more enjoyable experience. This discovery further emphasizes the need to engage and channel this natural instinct into effective learning strategies.
Cultivating a Curious Mindset in Education
In educational settings, fostering curiosity can lead to remarkable learning outcomes. Traditional teaching methods that prioritize rote memorization often stifle a student's natural inclination to explore concepts. Instead, educators can embrace teaching that prioritizes inquiry-based learning where students pose questions and engage in discussions. This approach not only satisfies their curiosity but also instills critical thinking skills.
Teachers can create a rich environment for curiosity by introducing real-world applications of the subjects being taught. For instance, rather than simply explaining scientific principles, educators can set up experiments that allow students to discover answers themselves. This type of experiential learning transforms passive reception of information into active participation, igniting a passion for discovery.
Encouraging collaboration can further enhance the cultivation of a curious mindset. Group projects and discussions empower students to share knowledge and explore diverse perspectives. This communal approach inspires learners to build upon each other's ideas and develop a collective curiosity that fosters a deeper understanding of a topic. It builds not only knowledge but also social skills that will prove beneficial in their future endeavors.
Assessment methods can also play a pivotal role in nurturing curiosity within the classroom. Instead of high-stakes exams that only test memorization, educators can implement formative assessments that allow for self-reflection and exploration. This lets students understand their learning process, promoting a mindset that values growth and continuous exploration rather than the fear of failing a test.
The Role of Environment in Enhancing Curiosity
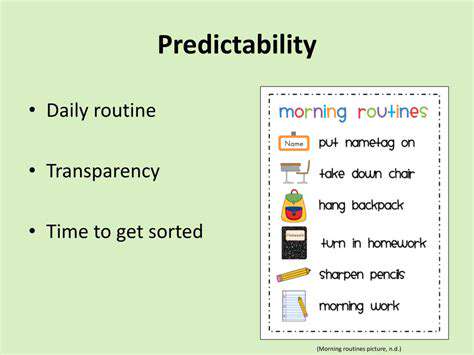
The physical and emotional environment significantly influences a person's natural curiosity and willingness to learn. Spaces that are stimulating and rich in resources can encourage exploration. For instance, classrooms filled with interactive materials, visual aids, and technology provide sensory experiences that can spark interest and engagement among students. These aspects are essential in making learning more appealing and accessible.
Moreover, creating a safe and supportive emotional climate is equally important. When learners feel safe to express their thoughts and questions, they are more likely to engage with the material. A supportive teacher who encourages dialogue and experimentation fosters a sense of belonging, making students more inclined to explore and take risks in their learning journey.
Parental involvement also plays a crucial role in fostering curiosity. When parents engage in their children’s learning, whether through discussions, reading together, or participating in activities, they send a message that learning is valued. This continued support at home can nurture a love for learning that extends beyond formal education into a lifelong pursuit of knowledge.
Communities can contribute positively by providing resources such as libraries, museums, and extracurricular programs that encourage exploration. When local environments are rich with opportunities to learn, individuals are more likely to take initiative and pursue interests that resonate with their innate curiosity. Collaborative efforts to build such environments can significantly benefit the collective learning landscape.
The Lifelong Impact of Nurturing Curiosity
Nurturing curiosity from an early age has profound implications on personal and professional development. Individuals who have developed a keen sense of curiosity throughout their lives often find themselves better equipped to adapt to change and innovate in their respective fields. Lifelong learning becomes a natural extension of their driven mindset, leading to greater career satisfaction and fulfillment.
Moreover, a person’s ability to ask questions and seek out answers is invaluable in a rapidly changing world. The skills developed through nurturing natural curiosity enable individuals to remain agile in the face of new challenges, whether technological, social, or economic. This agility can catalyze personal growth and pave the way for meaningful contributions to society.
Furthermore, fostering curiosity in others can create a ripple effect, where enthusiastic learners inspire those around them to explore and inquire as well. This communal engagement in learning establishes a culture of curiosity that can have lasting benefits not just for individuals, but for communities as a whole. The more we encourage and cultivate curiosity, the richer our social fabric becomes.
In conclusion, the inherent drive for learning, when recognized and nurtured, can unleash a lifetime of exploration and growth. By fostering environments that nurture curiosity, we create a future where continuous learning is not just an obligation but a joyful pursuit. The legacy of curiosity will be passed on through generations, shaping a culture that values innovation, creativity, and unending inquiry.
The Role of Parents and Educators
Empowering Children's Intrinsic Motivation
Nurturing natural curiosity is a crucial aspect of inspiring lifelong learning in children. Parents and educators play a significant role in fostering this curiosity by creating an environment that encourages exploration and discovery. This can be achieved by allowing children to make choices and take ownership of their learning, which in turn boosts their confidence and motivation. By doing so, children are more likely to develop a love for learning that extends beyond the classroom and into their daily lives. Moreover, parents and educators can facilitate this process by providing opportunities for children to engage in hands-on activities, ask questions, and explore their interests at their own pace. By doing so, children are able to develop a deep understanding of the world around them and are more likely to become lifelong learners.
Furthermore, parents and educators can also play a role in shaping children's attitudes towards learning by modeling curiosity themselves. When children see their parents or educators being curious and enthusiastic about learning, they are more likely to adopt these traits themselves. This can be achieved by sharing personal experiences, reading books together, and engaging in activities that promote learning and exploration. By doing so, children are able to see the value of learning and are more likely to develop a growth mindset that serves them well throughout their lives.
Additionally, parents and educators can also provide opportunities for children to take risks and make mistakes in a safe and supportive environment. This can be achieved by providing a safe space for children to experiment and try new things, without fear of failure. By doing so, children are able to develop resilience and perseverance, which are essential skills for lifelong learning. Furthermore, by allowing children to take risks and make mistakes, parents and educators can help them develop a sense of self-awareness and self-confidence that will serve them well in all areas of life.
Ultimately, empowering children's intrinsic motivation is key to inspiring lifelong learning. By creating an environment that encourages exploration and discovery, providing opportunities for children to take ownership of their learning, and modeling curiosity themselves, parents and educators can help children develop a love for learning that will stay with them throughout their lives.
Fostering a Growth Mindset
Fostering a growth mindset is essential for inspiring lifelong learning in children. A growth mindset is the belief that one's abilities and intelligence can be developed through hard work, dedication, and persistence. This mindset is in contrast to a fixed mindset, which believes that one's abilities are innate and cannot be changed. By fostering a growth mindset in children, parents and educators can help them develop a love for learning that is not dependent on external rewards or recognition.
Parents and educators can foster a growth mindset by praising effort rather than intelligence. For example, instead of saying "You're so smart!" they could say "You must have worked really hard on that!" This subtle difference in language can have a profound impact on a child's mindset and can help them develop a growth mindset. Additionally, parents and educators can also provide opportunities for children to reflect on their progress and set goals for themselves. By doing so, children are able to develop self-awareness and self-regulation skills that are essential for lifelong learning.
Furthermore, parents and educators can also provide opportunities for children to take on challenges that are slightly beyond their reach. This can be achieved by providing scaffolding support and guidance as needed. By doing so, children are able to develop resilience and perseverance, which are essential skills for lifelong learning. Additionally, by providing opportunities for children to take on challenges, parents and educators can help them develop a sense of self-efficacy that will serve them well in all areas of life.
Ultimately, fostering a growth mindset is key to inspiring lifelong learning. By praising effort rather than intelligence, providing opportunities for children to reflect on their progress and set goals for themselves, and providing opportunities for children to take on challenges that are slightly beyond their reach, parents and educators can help children develop a love for learning that will stay with them throughout their lives.
Avoiding Rigid Structures

The cornerstone of avoiding rigid structures in learning lies in the cultivation of a growth mindset, where individuals embrace the understanding that their abilities and intelligence are not fixed, but rather, are malleable and can be developed through dedication and hard work. This perspective is fundamentally different from a fixed mindset, which believes intelligence is static, potentially leading to a fear of challenges and a reluctance to embrace new experiences. Embracing this growth mindset empowers learners to view setbacks as opportunities for learning and improvement, fueling their natural curiosity and drive for lifelong learning, enabling them to navigate complexity with resilience and adapt to an ever-changing world. Cultivating this mindset requires a conscious effort to praise effort and process, rather than focusing solely on outcomes, highlighting the importance of perseverance and the value of the learning journey itself.
Furthermore, fostering a growth mindset involves creating an environment where mistakes are seen as valuable learning opportunities, encouraging risk-taking and experimentation without fear of judgment. This can be achieved through a variety of strategies, including providing constructive feedback, celebrating effort and progress, and modeling a positive attitude toward challenges. When learners feel safe to make mistakes and are supported in their efforts to learn and grow, they are more likely to persevere in the face of difficulties and to embrace new experiences with enthusiasm and curiosity, leading to a deeper and more meaningful learning experience. This supportive environment encourages them to explore different perspectives, which is essential for developing critical thinking skills and for fostering a genuine love of learning that extends far beyond the classroom.
To solidify this growth mindset, educators and parents should emphasize the importance of effort, strategies, and persistence over inherent ability, reframing challenges as opportunities for growth and learning. This requires shifting the focus from grades and performance to the learning process, encouraging students to reflect on their strategies, identify areas for improvement, and celebrate their progress. By emphasizing the process of learning and valuing effort, educators and parents can help students develop a resilient and adaptable approach to challenges, fostering a lifelong love of learning and a willingness to embrace new experiences with confidence and curiosity, ultimately empowering them to thrive in an ever-changing world.
Embracing Inquiry-Based Learning: Asking the Right QuestionsInquiry-based learning forms the bedrock of avoiding rigid learning structures by encouraging learners to formulate their own questions, investigate topics of interest, and construct their own understanding of the world. This learner-centered approach empowers students to take ownership of their learning, sparking their natural curiosity and fostering a deeper engagement with the subject matter. Instead of passively receiving information, learners become active participants in the learning process, driving their own exploration and discovery, leading to richer learning experiences that are personally meaningful and relevant to their lives and enabling them to retain information for a longer period of time.
The power of inquiry lies in its ability to cultivate critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, and the ability to analyze and evaluate information effectively. It's a method that transforms the classroom from a place of rote memorization to one of exploration and discovery. By framing learning around questions, educators encourage students to develop their own lines of inquiry, explore multiple perspectives, and critically evaluate information, thus transforming them into independent thinkers capable of navigating the complexities of the real world. This approach fosters not only content mastery but also the development of crucial skills that are essential for success in the 21st century and beyond, empowering them to become lifelong learners.
Implementing inquiry-based learning involves creating a learning environment that encourages exploration, experimentation, and collaboration, providing opportunities for learners to delve deeper into topics of personal interest. This may involve project-based learning, research projects, and other activities that encourage students to ask questions, investigate various sources of information, and draw their own conclusions. Through these explorations, students develop a love for learning, build confidence in their abilities, and develop the skills they need to succeed both inside and outside the classroom, paving the way for independent study and life-long knowledge acquisition.
Providing Flexible Learning EnvironmentsTo truly avoid rigid structures, it's critical to design flexible learning environments that cater to diverse learning styles and paces, adapting to individual student needs and preferences. Rigid classrooms often adopt a one-size-fits-all approach, which can leave many students feeling disengaged and frustrated, thereby hindering their ability to reach their full potential. Flexible environments, on the other hand, embrace a variety of instructional strategies, resources, and assessment methods, allowing students to learn in ways that best suit their individual needs and learning preferences. This adaptability is crucial for nurturing natural curiosity and fostering a lifelong love of learning, as it removes barriers and allows learners to engage with the material in ways that resonate with them.
Flexible learning can encompass a wide range of practices, including differentiated instruction, personalized learning paths, and the use of technology to provide customized learning experiences. This may involve offering students a choice of learning activities, providing varying levels of support, and allowing them to work at their own pace. Technology plays a crucial role in enabling flexible learning, allowing learners to access a wide range of resources, connect with peers and experts, and receive personalized feedback. This technology-integrated approach can break down traditional classroom barriers, enabling self-directed learning, deeper exploration, and personalized support.
Creating a flexible learning environment also necessitates a shift in the role of the teacher, from a sole knowledge provider to a facilitator of learning. This involves guiding students through the learning process, providing support and feedback, and fostering a culture of collaboration and self-reflection. The teacher's role becomes one of mentorship, encouragement, and guidance, creating a learning ecosystem that supports curiosity. This approach is about building relationships with students, understanding their individual needs and preferences, and working collaboratively with them to create a learning experience that is both challenging and rewarding.
Fostering Collaboration and Peer LearningCollaboration and peer learning provide an essential element to moving away from rigid educational models by creating opportunities for learners to share knowledge, challenge assumptions, and build upon each other's ideas. In traditional learning settings, students often work in isolation, limiting their opportunities to learn from others and develop vital social and communication skills. Collaborative learning environments, on the other hand, foster a sense of community and encourage learners to work together towards common goals, leading to a deeper understanding of the material and a greater sense of ownership of the learning process. This approach fosters a sense of camaraderie and mutual respect among students, as they learn to value different perspectives, share their ideas, and provide constructive feedback to one another, reinforcing the principles of teamwork and co-operation.
Peer learning involves students teaching and learning from each other, providing valuable opportunities for both the "teacher" and the "learner" to deepen their understanding. When students teach others, they are forced to articulate their understanding in clear and concise terms, which can help them to identify gaps in their knowledge and solidify their understanding of the material. Those who receive instruction from their peers benefit from hearing different perspectives, which challenges them to think critically about the material and consider multiple viewpoints. This can involve group projects, peer tutoring, and other activities that require students to work together, sharing information, and solving problems collaboratively, all of which are valuable assets in the real world and are essential for continuous learning and growth.
To effectively facilitate collaboration and peer learning, educators must create a classroom environment that is supportive, inclusive, and encourages risk-taking. This includes providing opportunities for students to work together, share their ideas, and provide constructive feedback to one another. Educators can guide the process by modeling effective communication skills, providing clear expectations, and facilitating group discussions. Through this approach, students develop not only content knowledge but also essential social skills and a deeper appreciation for the diverse perspectives that contribute to knowledge. This promotes a positive learning atmosphere, allowing for individual growth and shared experiences, ultimately strengthening the foundation for ongoing learning and intellectual exploration.
Embracing Real-World Applications and Contextual LearningIntegrating real-world applications and providing contextual learning experiences is a vital strategy in moving away from rigid educational structures and making learning more relevant and engaging. Too often, students are presented with abstract concepts and theoretical exercises that fail to connect with their lives or the world around them. By connecting learning to real-world problems, students become invested in the material, sparking their natural curiosity and increasing their motivation to learn, and the applications provide the context for that learning. This not only enhances their understanding of the subject matter but also equips them with the skills they need to succeed in their future careers and personal lives, enabling them to see the relevance of what they are learning.
Contextual learning involves placing learning experiences within a relevant context, such as a simulated work environment, a community project, or a real-world problem-solving activity. This approach allows students to see how the concepts they are learning apply in the real world and provides them with opportunities to practice these skills in authentic settings. This might involve field trips, guest speakers, project-based learning assignments, or other activities that connect learning to real-world experiences, which is also crucial in helping students build connections between their learning and their own interests and aspirations, thereby increasing their motivation and engagement, fostering a stronger understanding, and providing opportunities for practical application of knowledge.
To successfully incorporate real-world applications, educators should collaborate with community partners, industry professionals, and other experts to create authentic learning experiences. This might involve bringing in guest speakers, providing internships or apprenticeships, or organizing field trips to relevant sites, providing opportunities for students to learn from experts and to see how their learning applies in the real world. Creating authentic learning experiences, such as solving real-world problems, allows them to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills while making the learning process more engaging and meaningful, ultimately inspiring lifelong learning. This integration also demonstrates the practical value of education and gives students a sense of purpose, making their learning experience more relevant and impactful, which in turn, fosters curiosity and a deep appreciation for continuous growth and learning.
Encouraging Exploration and Experimentation
Fostering a Safe Environment for Inquiry
Creating a space where questions are encouraged is vital for exploration and experimentation. When learners feel safe to express their curiosity, they are more likely to engage in meaningful inquiries. This environment can be nurtured in classrooms, homes, or community spaces where dialogue and discussion are prioritized.
Adults can play a crucial role in maintaining this safe space by being responsive to the questions posed by learners. Instead of providing all the answers, facilitators can guide individuals to explore ideas further, promoting critical thinking and self-discovery. This approach encourages students to take ownership of their learning journey.
Incorporating diverse resources and materials within this environment can also foster exploration. Access to books, technology, and hands-on materials can expand the horizons of learners and encourage different modes of inquiry. The availability of varied tools promotes creativity and experimentation.
Additionally, promoting a culture of patience and perseverance can significantly enhance the learning environment. Mistakes and failures should be framed as opportunities for learning rather than setbacks. This attitude invites learners to experiment freely, knowing they won't be judged for the outcomes they achieve.
Ultimately, a safe environment for inquiry not only encourages exploration but also develops essential life skills such as resilience, adaptability, and critical thinking. As learners continue to explore their interests, they cultivate a love for lifelong learning, a pivotal aspect of personal and professional growth.
Encouragement Through Play and Discovery
Integrating play into the learning process is one of the most effective methods for fostering a spirit of exploration. Play not only stimulates creativity but also ignites curiosity among learners, allowing them to discover new concepts through hands-on experiences. This playful approach creates an engaging learning atmosphere that encourages experimentation.
For younger learners, open-ended play activities can lead to a wealth of questions and investigations. Children often engage in imaginative scenarios that promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Adults should leverage these opportunities to ask probing questions that guide further exploration while still allowing freedom of thought.
Incorporating outdoor exploration into educational settings can significantly enhance the learning experience. Nature acts as an excellent teacher, allowing learners to engage with their environment in ways that are both fun and educational. Observing local flora and fauna, weather patterns, or natural phenomena can inspire countless inquiries and experiments.
Multisensory experiences can boost interest and retention, especially for learners who may struggle with traditional learning methods. Activities that involve tactile, auditory, or visual elements can make concepts relatable and memorable. By embracing a play-based learning model, educators can inspire curiosity across various age groups.
Ultimately, encouraging exploration through play nurtures a sense of wonder and discovery. It provides learners with the freedom to ask questions, seek answers, and explore diverse perspectives. This exploration can lead to deeper understandings and the development of a lifelong learning mindset.
Promoting Reflective Practices
Reflection is a critical component of exploration and experimentation. By encouraging learners to take a step back and think about their experiences, they can better understand their learning processes and outcomes. Reflection helps individuals make sense of their inquiries and consider how they might apply their newfound knowledge in real-world contexts.
To promote reflective practices, educators can implement journaling or portfolio systems. These tools allow learners to document their thoughts, questions, and experiences. Regularly reviewing these entries can highlight patterns in their thinking and areas for further exploration, leading to an enriched understanding of their learning process.
Additionally, group discussions and peer feedback sessions can foster a collaborative reflective practice. Engaging with peers about their experiences can offer new insights and perspectives, encouraging learners to rethink their approaches and consider alternative viewpoints. This collective reflection can inspire deeper levels of curiosity.
Mentorship plays an essential role in promoting reflection. By pairing learners with experienced mentors or facilitators, they can receive tailored guidance and support. Mentors can help learners navigate challenges and encourage them to reflect on their growth, driving an ongoing cycle of exploration and learning.
Ultimately, fostering reflective practices cultivates a strong foundation for lifelong learning. As learners become more aware of their thought processes and the implications of their inquiries, they develop a sense of ownership over their education. This awareness is key to inspiring and sustaining a natural curiosity throughout their lives.
Creating Meaningful Learning Experiences

Creating learning experiences that spark genuine curiosity necessitates the establishment of inquiry-based environments, where students are empowered to ask questions, explore their own interests, and construct their own understanding. This paradigm shift moves away from rote memorization and towards active participation, allowing students to become the drivers of their own learning journeys, encouraging them to think critically and solve problems creatively. Allowing children to delve into subjects that capture their imaginations is a crucial aspect of nurturing their inherent desire to learn, providing them with opportunities to delve deeper into topics that resonate with their individual passions, cultivating a lifelong love of knowledge and discovery.
One effective strategy for fostering an inquiry-based environment involves providing students with open-ended questions or scenarios that stimulate their curiosity and prompt them to investigate further. These prompts can range from posing intriguing scientific phenomena to presenting complex social issues, challenging students to develop their own hypotheses, gather evidence, and draw their own conclusions. Furthermore, incorporating real-world problems and case studies into the curriculum can bring learning to life, allowing students to see the practical applications of their knowledge and the relevance of their skills, bridging the gap between theoretical concepts and practical application, making learning more meaningful and memorable.
Providing access to diverse resources, including books, articles, videos, and digital tools, is another crucial element in supporting inquiry-based learning, empowering students to gather information from multiple perspectives and engage in independent research. Encouraging collaborative projects and group discussions helps students share their findings, challenge each other's ideas, and build upon each other's knowledge, promoting a dynamic learning environment where students learn from one another, developing essential communication and teamwork skills. Furthermore, designing projects that encourage hands-on experimentation and investigation allows students to engage directly with the material, experiencing the joys of discovery firsthand, and solidifying their understanding through practical application, which will contribute to increased student engagement.
Teachers should act as facilitators and guides, providing support and resources while encouraging students to take ownership of their learning, allowing them to experience the journey of self-discovery. This involves creating a classroom culture that values questions, experimentation, and making mistakes, recognizing that errors are an integral part of the learning process, and providing constructive feedback that supports continued growth. This also includes modeling a lifelong love of learning by demonstrating a genuine curiosity for new ideas and experiences, which will encourage students to embrace a similar mindset, instilling in them a sense of wonder and a desire to learn throughout their lives.
Assessment methods should also align with the principles of inquiry-based learning, focusing on evaluating students' ability to think critically, solve problems, and communicate their ideas effectively rather than simply recalling facts. This can involve using projects, presentations, and portfolios to assess student learning, providing students with opportunities to demonstrate their understanding in creative and meaningful ways, and creating a sense of ownership over their learning. The goal is not to simply measure knowledge but to provide students with chances to develop and express their unique talents, allowing them to reflect on their growth and identify areas for improvement.
Cultivating a Growth Mindset and Embracing ChallengesNurturing a growth mindset, which involves believing that intelligence and abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work, is essential for inspiring lifelong learning. Encouraging students to embrace challenges as opportunities for growth and to view mistakes as valuable learning experiences can significantly impact their willingness to persevere in the face of difficulties, which contributes to the development of resilience and a persistent approach to problem-solving. Promoting a growth mindset can involve celebrating effort and progress rather than just focusing on outcomes, providing specific and constructive feedback, and creating a supportive classroom environment where students feel safe to take risks and make mistakes without fear of judgment.
One key strategy for cultivating a growth mindset involves teaching students about the brain and how it learns. By explaining that the brain is like a muscle that can be strengthened through practice and effort, students can develop a belief in their own potential and a willingness to embrace challenges. Furthermore, providing students with strategies for managing setbacks and developing perseverance can equip them with the tools they need to overcome obstacles and achieve their goals, which will contribute to their overall confidence and academic success. Using real-life examples of successful individuals who have overcome challenges can also provide inspiration and motivation for students.
Creating a culture of celebrating effort and perseverance can also help foster a growth mindset. Recognizing and rewarding students for their hard work, dedication, and willingness to embrace challenges, regardless of the outcome, can encourage them to continue striving for improvement, even when they face difficulties, which can contribute to building internal motivation. Providing regular opportunities for students to reflect on their learning processes, identify areas where they have grown, and set new goals can also promote a growth mindset, encouraging them to view learning as a continuous journey of self-improvement.
Encouraging students to embrace challenges involves creating opportunities for them to step outside of their comfort zones and try new things, which can foster a sense of resilience and self-efficacy. This can involve presenting students with challenging projects, providing them with opportunities to collaborate with peers on complex problems, or encouraging them to participate in extracurricular activities that push their boundaries, such as participating in debates or joining a science club. Helping students develop problem-solving skills will allow them to approach challenges in a logical and strategic way, breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps, and implementing different solutions.
Finally, providing students with opportunities to receive and give constructive feedback is crucial in fostering a growth mindset. Creating a culture where students feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and ideas, as well as providing feedback to their peers, can promote a sense of collaboration and mutual support. Offering students specific and actionable feedback that highlights areas for improvement, as well as providing encouragement, can help them develop a positive attitude toward learning and a belief in their own ability to succeed, which will also increase their confidence. Regular feedback sessions, peer reviews, and self-reflection exercises all serve this purpose, promoting continual learning and improvement.
Connecting Learning to Real-World Applications and Student InterestsTo truly inspire lifelong learning, it's crucial to connect classroom learning to real-world applications and student interests, demonstrating the relevance and practicality of what is being taught. This can involve incorporating case studies, simulations, and field trips into the curriculum, providing students with opportunities to see how the concepts they are learning are applied in various industries and contexts. This also involves encouraging students to identify their own passions and interests and to explore how these relate to their learning, allowing them to personalize their learning experiences and connect them to their own lives, making the subject more engaging and memorable.
One effective strategy for connecting learning to the real world is to incorporate current events and real-life examples into lessons, allowing students to see how the concepts they are learning are relevant to the world around them. This can involve discussing current scientific discoveries, analyzing political debates, or exploring social issues that are relevant to their lives. Bringing guest speakers from different fields into the classroom, such as scientists, artists, entrepreneurs, and professionals from various fields, can also provide students with firsthand insights into how knowledge and skills are applied in practice, allowing them to learn from different perspectives and gain a deeper understanding of their chosen field.
Encouraging student-led projects and allowing students to choose topics that align with their interests can significantly increase engagement and motivation. This might involve allowing students to select their own research topics, design their own experiments, or create their own projects related to the course material, fostering a sense of ownership and allowing them to explore their passions. This personalization makes learning more meaningful, and it provides students with the opportunity to develop their unique talents and express their creativity. Providing students with the opportunity to connect with people outside of the school, such as mentors, professionals, and community members, can further expand their horizons and expose them to new ideas.
Incorporating service-learning projects can also provide students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills to address real-world problems and make a positive impact on their communities. This can involve participating in environmental cleanup projects, volunteering at local organizations, or raising awareness about social issues. Involving students in these hands-on activities allows them to see the real-world impact of their learning, promoting a sense of purpose and inspiring them to continue learning and growing. Giving students the freedom to choose projects that will contribute to their communities and impact their personal growth allows them to develop a deeper understanding of their roles as active citizens.
Assessing learning in ways that reflect real-world applications is also crucial. This can involve using performance-based assessments, such as presentations, projects, and portfolios, to evaluate students' ability to apply their knowledge and skills to solve authentic problems. Creating opportunities for students to share their work with a wider audience, such as presenting at conferences or publishing their work online, can also further motivate them to produce high-quality work, encouraging them to think critically and creatively, and making their efforts more meaningful. Moreover, assessing learning in ways that mirror the challenges and opportunities encountered in real-world settings can help students to cultivate critical thinking skills and develop the adaptability needed for success in various aspects of life.
The Importance of Play
The Multifaceted Benefits of Play for Cognitive Development
Play, often perceived as a frivolous pastime, is, in reality, a cornerstone of cognitive development, particularly in early childhood. Through engaging in playful activities, children actively explore their environment, experiment with different concepts, and learn to problem-solve in dynamic and often unpredictable ways. This hands-on exploration cultivates crucial skills like critical thinking, spatial reasoning, and the ability to adapt to novel situations, all of which are foundational for academic success and intellectual growth throughout their lives, showcasing the intrinsic value of play as a learning mechanism and a catalyst for intellectual exploration and development.
Furthermore, the inherent social dimensions of play provide invaluable opportunities for children to hone their communication and interpersonal skills. Whether through cooperative games, imaginative role-playing, or simply sharing toys, children learn to negotiate, compromise, and understand the perspectives of others. These social interactions are paramount in fostering empathy, building strong relationships, and navigating the complexities of social dynamics, thereby equipping children with the emotional intelligence needed to thrive in diverse social settings and collaborative environments both now and in the future, solidifying the crucial role of play in holistic development beyond intellectual pursuits.
The act of play also stimulates creativity and imagination, encouraging children to think outside the box and generate novel solutions to challenges. Through imaginative scenarios and make-believe worlds, children can experiment with different roles, explore their emotions, and develop a sense of agency and self-expression. This creative freedom is instrumental in nurturing innovation, fostering a love for exploration, and promoting a sense of wonder about the world, all essential ingredients for lifelong learning and adaptability in an ever-evolving society, demonstrating the profound connection between play and the capacity for creative thinking and innovative solutions.
Play as a Catalyst for Emotional and Social Well-being
Beyond its cognitive benefits, play plays a pivotal role in fostering emotional and social well-being, providing a safe and supportive environment for children to express their feelings and manage their emotions. Through various play activities, children learn to regulate their impulses, cope with frustration, and develop resilience in the face of challenges. The ability to navigate emotional complexities is crucial for building self-esteem, fostering mental health, and promoting overall well-being, thereby highlighting the deep connection between play and the development of emotional regulation and self-awareness, laying the groundwork for psychological resilience.
Additionally, engaging in play allows children to develop strong social bonds, learn to collaborate with others, and establish a sense of belonging within a group. Cooperative games and shared play experiences offer opportunities to develop essential social skills like communication, negotiation, and conflict resolution. These social interactions are critical in forming lasting friendships, building a sense of community, and developing the social intelligence needed to navigate the complexities of human relationships, reinforcing the significant impact of play on social development and the formation of meaningful connections with peers, thus establishing a foundation for strong social and interpersonal skills.
The freedom and spontaneity inherent in play can also reduce stress and anxiety, providing children with a much-needed outlet to unwind and recharge. Playful activities provide a sense of control and agency, allowing children to temporarily escape the pressures of their daily lives and express themselves freely without judgment or fear of failure. This sense of freedom and joy promotes emotional balance, enhances overall happiness, and contributes to a more positive outlook on life, showcasing the importance of play in fostering a healthy emotional state and providing a buffer against the stresses and anxieties of childhood, effectively supporting emotional resilience.