Exploring the Environmental Impact of Urbanization on Biodiversity
Introduction to Urbanization and Its Effects

Understanding Urbanization
Urbanization is the process by which cities grow as a result of population migration from rural to urban areas. This phenomenon leads to the development of urban infrastructures such as housing, roads, and commercial centers. As urban areas expand, they often encroach upon natural habitats, significantly altering local ecosystems.
With an increasing global population, more people are gravitating towards cities in search of better opportunities. This trend is expected to continue, leading to further urban sprawl. It's essential to grasp the implications of urbanization on the environment to mitigate its adverse effects.
City life brings with it conveniences and advancements, but at a cost. The integration of human activity within previously untouched landscapes can disrupt biodiversity and threaten species survival.
The Impact of Urbanization on Natural Habitats
As urban areas expand, many natural habitats are destroyed or fragmented. This fragmentation can lead to isolated populations of flora and fauna, which affects their ability to reproduce and survive. The loss of these habitats can have a cascading effect on local biodiversity.
Urbanization often leads to the introduction of invasive species that can outcompete native species for resources. Invasive plants and animals can disrupt local food webs, causing declines in native species. Such changes can threaten the delicate balance of ecosystems that have evolved over millennia.
Moreover, the urban heat island effect increases temperatures in cities, further stressing the local environment. Increased temperatures can alter species distributions and even lead to the extinction of sensitive species that are unable to adapt.
Effects of Pollution on Biodiversity
Urban areas are often major sources of various types of pollution, including air, water, and soil contamination. These pollutants can have dire effects on the health of both urban and nearby natural ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems, in particular, suffer due to runoff that carries harmful substances into water bodies.
Air pollution can directly impact the health of urban wildlife, diminishing their survival rates. Animals that are particularly sensitive to changes in air quality may struggle to find sufficient food and shelter. Pollutants can accumulate in the food chain, affecting not just individual species but entire ecosystems.
In addition to direct impacts, pollution also affects the reproductive capabilities of various species. As pollution levels rise, the genetic integrity of populations can decrease, leading to reduced fertility and increased vulnerability.
Urban Green Spaces and Biodiversity Conservation
Despite the challenges posed by urbanization, urban green spaces can play a pivotal role in supporting biodiversity. Parks, gardens, and green roofs can serve as critical habitats for numerous species. These areas can act as refuges for wildlife, allowing them to thrive amidst urban surroundings.
Creating and maintaining urban green spaces can help link fragmented habitats, allowing for greater movement and migration of species. These connections are crucial for species' survival, especially as climate change continues to alter natural environments.
Moreover, urban green spaces can enhance local climate resilience by improving air quality and reducing urban heat. They also provide recreational opportunities for residents, fostering a sense of community and connection to nature.
Strategies for Sustainable Urban Development
Sustainable urban development seeks to minimize the negative impacts of urbanization on biodiversity. This can involve implementing strategies like green infrastructure, which integrates natural systems into urban planning. Initiatives may include rain gardens, permeable pavements, and green corridors.
Another effective approach is engaging communities in conservation efforts. Educational programs that promote awareness about local wildlife can galvanize public support for biodiversity conservation within urban landscapes. When communities are involved, the effectiveness of conservation measures tends to increase dramatically.
Finally, involving policymakers in biodiversity-friendly practices is key. By prioritizing sustainable development policies, cities can balance growth while maintaining ecological integrity, ultimately supporting both human and wildlife populations in harmony.
The Connection Between Urban Growth and Habitat Loss

The Mechanisms of Habitat Destruction
Urbanization leads to significant changes in land use, primarily through the conversion of natural landscapes into residential, commercial, and industrial areas. This transformation can obliterate essential habitats for many species, leading to decreased biodiversity. As urban areas expand, the native flora and fauna are often replaced with non-native species that can outcompete the indigenous organisms.
Moreover, urban sprawl frequently results in the fragmentation of ecosystems. Isolated habitats limit the movement and genetic exchange between populations, making it more challenging for species to thrive. This scenario can create "ecological islands," where wildlife is unable to find suitable mates, food sources, or shelter, ultimately pushing them toward extinction.
The Role of Policy and Planning in Mitigating Impacts
Effective urban planning can play a crucial role in mitigating the adverse effects of urbanization on biodiversity. By integrating green spaces such as parks, gardens, and green roofs into city designs, planners can help maintain ecosystems and provide crucial habitats. These spaces act as refuges for various species, enhancing the overall ecological health of urban environments.
Additionally, policies aimed at preserving natural areas and promoting sustainable development are essential. Implementing regulations that protect critical habitats from urban encroachment can significantly contribute to the conservation of biodiversity in urban areas. Collaboration between governmental bodies, non-profit organizations, and local communities is vital in fostering an environment where urban growth and biodiversity can coexist.
Pollution: A Byproduct of Urban Expansion
The Sources of Urban Pollution
Urban environments generate a variety of pollutants that can significantly affect local biodiversity. Common sources include vehicular emissions, industrial discharges, and construction activities. These pollutants often release harmful substances into the air and waterways, leading to deterioration of ecosystems.
For example, heavy metals and chemicals used in manufacturing processes can seep into nearby soils and bodies of water, severely impacting flora and fauna. As urban areas continue to expand, understanding the origins of these pollutants becomes crucial for effective management and mitigation strategies.
Impact of Air Pollution on Flora and Fauna
Air pollution in urbanized areas often leads to the degradation of plant life. Ozone, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter interfere with photosynthesis and growth, making it difficult for plants to thrive. This can lead to a decline in local vegetation, which is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance.
Animals are also affected, as many rely on these plants for food and shelter. As air quality diminishes, species may decline or even become extinct, further exacerbating biodiversity loss in urban contexts.
Water Pollution and Its Consequences
Urbanization frequently results in increased runoff that introduces pollutants into nearby water bodies. Stormwater systems in cities can carry oil, heavy metals, and debris directly into rivers and lakes, posing a threat to aquatic life. These pollutants compromise water quality, making it unsuitable for both human use and wildlife survival.
Strategies for Reducing Urban Pollution
To combat the pollution arising from urban expansion, cities must adopt sustainable practices and policies. One effective approach is the implementation of green infrastructure, such as green roofs, permeable pavements, and urban forests, which can help filter pollutants and improve air and water quality.
Additionally, promoting public transportation and vehicle emissions regulations can decrease the volume of pollutants released into the environment. Encouraging community involvement and education on pollution prevention is also critical for fostering a culture of sustainability among urban residents.
The Role of Biodiversity in Mitigating Pollution
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in the health of urban ecosystems and can help mitigate the effects of pollution. Diverse plant species, for instance, can absorb carbon dioxide and filter pollutants, improving overall air quality. This balance is essential for fostering a resilient urban environment that can withstand the pressures of growth.
The Impact on Climate Change
The Role of Urbanization in Climate Change
Urbanization significantly contributes to climate change as cities expand and develop. The aggregation of population and industries leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from transportation, energy consumption, and waste production.
As urban areas grow, natural landscapes are replaced with impervious surfaces like concrete and asphalt, which alter local climates. These changes can create urban heat islands, where temperatures are consistently higher than in rural areas, further exacerbating climate issues.
The demand for energy in urban settings is also higher, leading to greater reliance on fossil fuels. This increased energy consumption produces large amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants, which directly influence global warming.
Moreover, urban environments often disrupt the natural carbon sequestration process that occurs in forests and wetlands. The loss of green spaces means fewer plants to absorb CO2, reducing the overall carbon sink capacity of the region.
Collectively, these factors illustrate how urbanization is a driving force behind climate change, emphasizing the necessity for sustainable city planning and management practices.
Effects of Urban Sprawl on Natural Habitats
Urban sprawl leads to the significant fragmentation of natural habitats, placing immense pressure on biodiversity. As cities seek to accommodate growing populations, forests, wetlands, and grasslands are often cleared or degraded, resulting in the loss of critical ecosystems.
This habitat fragmentation not only reduces the available space for wildlife but also isolates species populations, making it difficult for them to breed and thrive. This isolation can lead to inbreeding and reductions in genetic diversity, making species more vulnerable to disease and environmental changes.
Furthermore, the encroachment of urban areas into natural ecosystems often leads to increased human-wildlife conflict. As animals lose their habitats, they may venture into urban settings in search of food and shelter, which can lead to harmful situations for both wildlife and humans.
Conservation efforts in urban settings are crucial. Strategies such as creating green corridors and wildlife reserves within city limits can help mitigate some of the negative impacts of urban sprawl, allowing for species migration and survival.
In conclusion, recognizing and addressing the effects of urban sprawl on natural habitats is essential for preserving biodiversity in the face of continued urbanization.
Urban Pollution and Its Impact on Biodiversity
Urban pollution from various sources, including vehicles, industrial activities, and waste disposal, poses a significant threat to biodiversity. Contaminants released into the air, water, and soil can have dire consequences for both plant and animal life.
Air pollution, particularly from transportation and industrial emissions, can lead to respiratory problems in wildlife and disrupt ecological balance. Species that are sensitive to air quality may experience population declines as their habitats become increasingly inhospitable.
Water pollution, often resulting from urban runoff, can have devastating effects on aquatic ecosystems. Pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and chemicals can contaminate water bodies, leading to the loss of sensitive species and degrading water quality.
Soil contamination due to improper waste disposal practices can also impact terrestrial biodiversity. Polluted soils affect plant growth and can bioaccumulate harmful substances within the food chain, posing risks to both wildlife and humans who rely on these ecosystems for food and resources.
Addressing urban pollution through better regulations and sustainable practices is vital for protecting biodiversity in urban landscapes. Clean air and water initiatives, alongside responsible waste management strategies, are essential components of urban ecological health.
Integrating Biodiversity into Urban Planning
Incorporating biodiversity considerations into urban planning is essential for fostering sustainable cities. A proactive approach to urban development can help protect and even enhance local ecosystems while accommodating population growth and infrastructure needs.
Urban planners can implement strategies like green roofs, vertical gardens, and biodiversity corridors that promote the coexistence of urban environments with natural ecosystems. Such features not only improve biodiversity but also enhance urban aesthetics and quality of life for residents.
Community engagement in biodiversity initiatives is crucial. Residents can be involved in creating and maintaining green spaces, participating in wildlife surveys, and educating others on the importance of local ecosystems. This grassroots involvement fosters a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards the environment.
Additionally, policies that encourage the preservation of existing green spaces, the restoration of degraded habitats, and the cultivation of native plant species can help support urban biodiversity. These practices contribute not only to ecological balance but also to the overall health and well-being of urban populations.
Ultimately, the integration of biodiversity in urban planning serves as a foundational step towards creating resilient cities that recognize the intrinsic value of nature in our increasingly urbanized world.
Mitigation Strategies for Reducing Environmental Impact
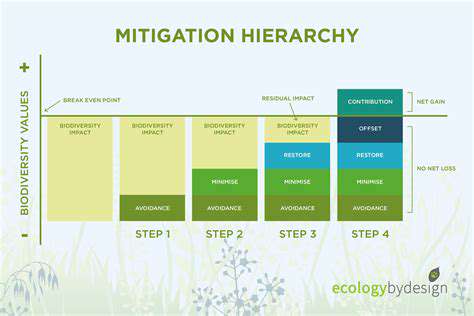
1. Implementing Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure refers to a network of natural and semi-natural systems that provide environmental benefits, such as stormwater management, air quality improvement, and temperature regulation.
This approach helps in creating urban spaces that promote biodiversity while mitigating the effects of urbanization. By integrating parks, green roofs, and vertical gardens into urban design, municipalities can significantly enhance habitat availability for various species.
Additionally, green corridors can connect isolated ecosystems, allowing wildlife to thrive despite urban barriers.
Innovative designs like permeable pavements also contribute to reducing runoff and improving water quality, further supporting local ecosystems.
Incorporating these strategies into city planning not only preserves biodiversity but also enhances the quality of life for urban residents.
2. Promoting Sustainable Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning focuses on the long-term viability of urban areas by considering environmental, social, and economic factors in development decisions.
By adopting a holistic approach, city planners can create spaces that benefit both the ecosystem and the community. Zoning laws can be reformed to prioritize green spaces and limit the extent of urban sprawl.
Public transport systems should be expanded to reduce reliance on cars, thereby decreasing pollution and habitat destruction caused by road expansion.
Community involvement plays a crucial role in sustainable urban planning, as local knowledge and collaboration can lead to more effective conservation practices.
Ultimately, fostering a culture of sustainability within urban population can drive systemic changes that protect biodiversity while accommodating growth.
